With the continuous evolution of LED materials and packaging technology, the brightness of LED products continues to increase, and the application of LED is becoming more and more widespread. Using LED as the backlight source of displays has become a hot topic recently, mainly different types of LED backlight technology It has advantages over traditional cold cathode tubes (CCFL) in terms of color, brightness, lifespan, power consumption and environmental protection requirements, attracting industry players to actively invest.Today qihe smt pick and place machine sharing the secret of heat dissipation in LED heat dissipation design .
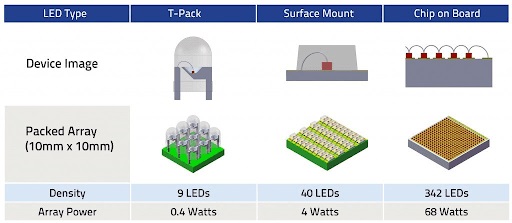
The initial single-chip LED did not have high power, limited heat generation, and was not a big thermal problem, so its packaging method was relatively simple. However, in recent years, with the continuous breakthroughs in LED material technology, LED packaging technology has also changed, gradually developing from early single-chip cannon-shaped packaging to flat, large-area multi-chip packaging modules;
The operating current has progressed from the early low-power LEDs of about 20mA to the current high-power LEDs of about 1/3 to 1A. The input power of a single LED is as high as more than 1W, and even to 3W and 5W packaging methods.
Since the thermal issues derived from high-brightness and high-power LED systems will be the key to product functionality, to quickly dissipate the heat generated by LED components to the surrounding environment, we must first start with thermal management at the packaging level (L1 & L2).
The current industry practice is to connect the LED chip to a heat sink with solder or thermal paste, and reduce the thermal impedance of the package module through the heat spreader. This is also the most common LED package module currently on the market. The main sources include Lumileds, Internationally renowned LED manufacturers such as OSRAM, Cree and Nicha.
Many terminal application products, such as mini projectors, automotive and lighting sources, require more than thousands or tens of thousands of lumens in a specific area. Single-chip packaging modules alone are obviously not enough to cope with this problem. , moving towards multi-chip LED packaging, and direct bonding of chips to substrates is the future development trend.
Thermal dissipation problem is the main obstacle in the development of LEDs for lighting objects. The use of ceramics or heat pipes is an effective way to prevent overheating, but thermal management solutions increase the cost of materials. The purpose of high-power LED thermal management design is to effectively reduce Thermal resistance between chip heat dissipation and final product,
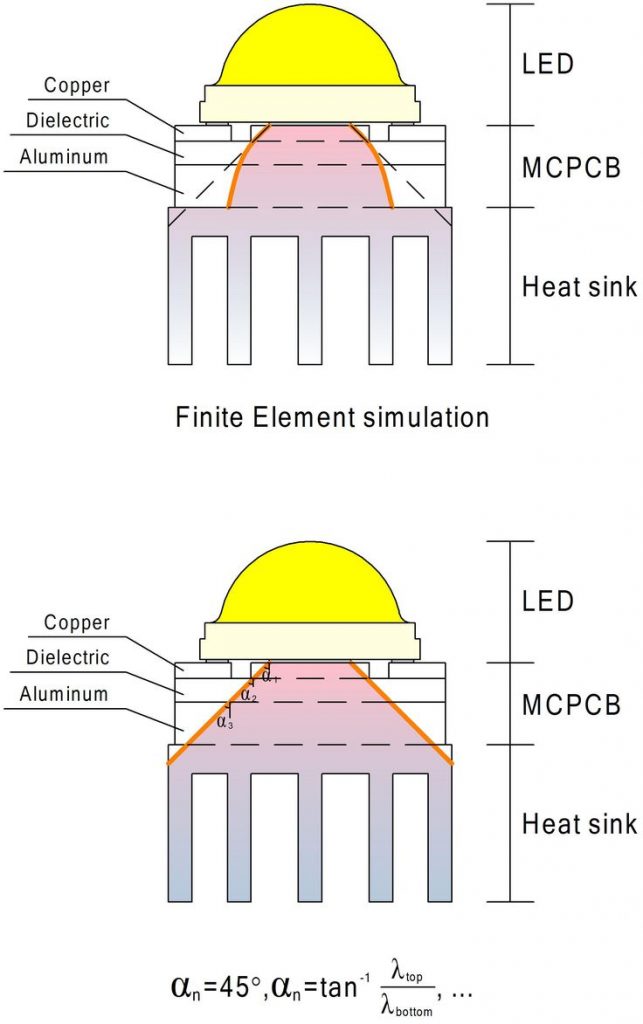
R junction-to-case is a material-based solution that provides low thermal resistance but high conductivity, allowing heat to be transferred directly from the chip to the outside of the package shell through die attach or hot metal methods.
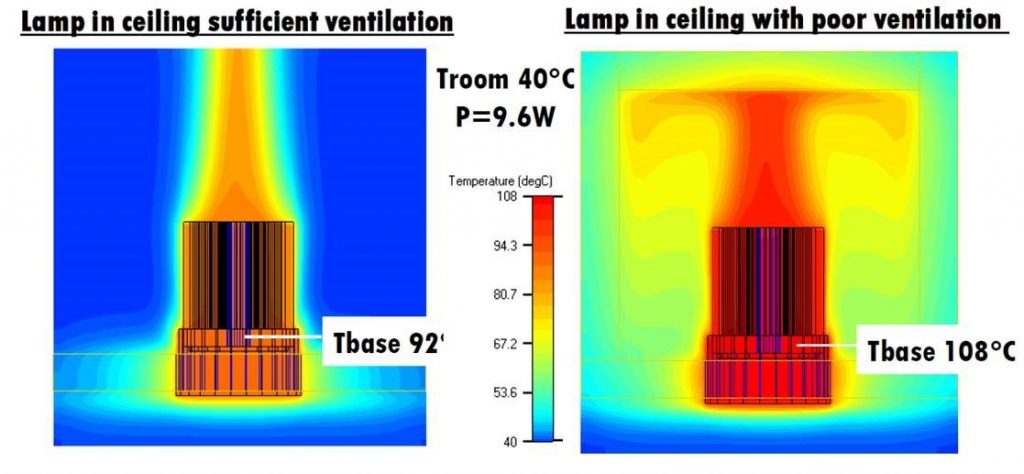
Of course, LED heat dissipation components are similar to CPU heat dissipation. They are mainly air-cooling modules composed of heat sinks, heat pipes, fans and thermal interface materials. Of course, water cooling is also one of the thermal countermeasures. Taking the current most popular large-size LED TV backlight modules, the input power of 40-inch and 46-inch LED backlights is 470W and 550W respectively. Considering that 80% of it is converted into heat, the required heat dissipation is about Around 360W and 440W.
So how to take away this heat? Currently, the industry uses water cooling for cooling, but there are concerns about high unit price and reliability. Heat pipes are also used in conjunction with heat sinks and fans for cooling, such as the 46-inch LED backlight LCD TV from the Japanese manufacturer SONY, but the fan consumes power and Issues such as noise still exist. Therefore, how to design a fanless cooling method may be an important key to determining who will win in the future.
Below we will introduce several heat dissipation methods and heat dissipation materials.
Heat dissipation method
Generally speaking, according to the way heat is taken away from the radiator, radiators can be divided into active cooling and passive cooling. The so-called passive heat dissipation means that the heat of the heat source LED light source is naturally dissipated into the air through the heat sink. The heat dissipation effect is proportional to the size of the heat sink.
However, because it dissipates heat naturally, the effect is of course greatly reduced. It is often used in equipment that does not require space, or to dissipate heat for components that do not generate much heat. For example, some popular motherboards also use passive heat dissipation on the north bridge, which is absolutely Most adopt active cooling. Active cooling is to forcefully take away the heat emitted by the heat sink through cooling equipment such as fans. It is characterized by high heat dissipation efficiency and small smt pick and place equipment size.
Active cooling, subdivided in terms of heat dissipation methods, can be divided into air-cooled heat dissipation, liquid cooling heat dissipation, heat pipe heat dissipation, semiconductor refrigeration, chemical refrigeration, etc.
Air-cooling
Air-cooling is the most common way of heat dissipation, and it is also a cheaper way in comparison. Air cooling essentially uses a fan to take away the heat absorbed by the radiator. It has the advantages of relatively low price and easy installation. However, it has a high dependence on the environment. For example, its heat dissipation performance will be greatly affected when the temperature rises and when overclocking.
Liquid-cooling
Liquid-cooling heat dissipation takes away the heat from the radiator through forced circulation of liquid driven by a pump. Compared with air cooling, it has the advantages of being quiet, stable cooling, and less dependent on the environment. The price of liquid cooling is relatively high, and installation is relatively troublesome. At the same time, when installing, try to follow the instructions in the instruction manual to obtain the best heat dissipation effect. Due to cost and ease of use considerations, liquid cooling usually uses water as the heat transfer liquid, so liquid cooling radiators are often called water cooling radiators.
Heat pipe
The heat pipe is a heat transfer element that makes full use of the principle of heat conduction and the rapid heat transfer properties of the refrigerant medium. It transfers heat through the evaporation and condensation of liquid in a fully enclosed vacuum tube. It has extremely high thermal conductivity and good isothermal properties. The heat transfer area on both sides of the hot and cold sides can be changed arbitrarily, the heat can be transferred over long distances, and the temperature can be controlled. The heat exchanger composed of heat pipes has high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, and low fluid resistance loss. advantage. Its thermal conductivity far exceeds that of any known metal.
Semiconductor refrigeration
Semiconductor refrigeration uses a special semiconductor refrigeration chip to generate a temperature difference when energized. As long as the heat at the high temperature end can be effectively dissipated, the low temperature end will be continuously cooled. A temperature difference is generated on each semiconductor particle. A cooling chip is composed of dozens of such particles connected in series, thereby forming a temperature difference on the two surfaces of the cooling chip. Utilizing this temperature difference phenomenon and using air cooling/water cooling to cool down the high-temperature end can achieve excellent heat dissipation effects. Semiconductor refrigeration has the advantages of low refrigeration temperature and high reliability. The cold surface temperature can reach below minus 10°C. However, the cost is too high and it may cause short circuit due to too low temperature. Moreover, the current semiconductor refrigeration chip technology is not mature enough. practical.
Chemical refrigeration
The so-called chemical refrigeration is to use some ultra-low temperature chemicals to absorb a large amount of heat when melting to reduce the temperature. In this regard, the use of dry ice and liquid nitrogen is more common. For example, dry ice can be used to reduce the temperature to below minus 20 degrees Celsius, and some more “perverted” players use liquid nitrogen to reduce the CPU temperature to below minus 100 degrees Celsius (theoretically). Of course, due to its high price and short duration, this This method is mostly found in laboratories or extreme overclocking enthusiasts.
Material selection
Thermal conductivity coefficient (unit: W/mK)
Silver 429
Copper 401
Gold 317
Aluminum 237
Iron 80
Lead 34.8
Type 1070 aluminum alloy 226
Type 1050 aluminum alloy 209
Type 6063 aluminum alloy 201
Type 6061 aluminum alloy 155
Generally speaking, ordinary air-cooled radiators naturally choose metal as the material of the radiator. For the selected material, it is hoped that it has both high specific heat and high thermal conductivity. From the above, it can be seen that silver and copper are the best thermal conductive materials, followed by gold and aluminum. But gold and silver are too expensive, so currently heat sinks are mainly made of aluminum and copper.smt pick and place
In comparison, both copper and aluminum alloys have their own advantages and disadvantages: copper has good thermal conductivity, but it is more expensive, difficult to process, too heavy, and copper radiators have a small heat capacity and are easy to oxidize. . On the other hand, pure aluminum is too soft to be used directly. Only the aluminum alloy used can provide sufficient hardness. The advantages of aluminum alloy are low price and light weight, but the thermal conductivity is much worse than that of copper. Therefore, in the development history of radiators, products made of the following materials have also appeared:
Pure aluminum radiators
Pure aluminum radiators were the most common radiators in the early days because of their simple manufacturing process and low cost. So far, pure aluminum radiators still occupy a considerable part of the market. In order to increase the heat dissipation area of its fins, the most commonly used processing method for pure aluminum radiators is aluminum extrusion technology, and the main indicators for evaluating a pure aluminum radiator are the thickness of the radiator base and the Pin-Fin ratio. Pin refers to the height of the fins of the heat sink, and Fin refers to the distance between two adjacent fins. The Pin-Fin ratio is the height of the Pin (excluding the thickness of the base) divided by the Fin. The larger the Pin-Fin ratio means the larger the effective heat dissipation area of the radiator, which means the more advanced the aluminum extrusion technology. Pure copper radiator smt pick and place
The thermal conductivity of copper is 1.69 times that of aluminum, so under the same conditions, a pure copper radiator can take away heat from the heat source faster. However, the quality of copper is a problem. Many radiators advertised as “pure copper radiators” are not actually 100% copper. In the list of copper, those with a copper content of more than 99% are called acid-free copper, and the next grade of copper is red copper with a copper content of less than 85%. Most pure copper radiators currently on the market have a copper content somewhere in between. Some inferior pure copper radiators contain less than 85% copper.
Although the cost is very low, their thermal conductivity is greatly reduced, affecting heat dissipation. In addition, copper also has obvious shortcomings, such as high cost, difficulty in processing, and large radiator mass, which hinder the application of all-copper heat sinks. The hardness of red copper is not as good as aluminum alloy AL6063, and certain mechanical processing (such as trenching, etc.) performance is not as good as aluminum; the melting point of copper is much higher than that of aluminum, which is not conducive to extrusion (Extrusion) and other issues.
Copper-aluminum bonding technology
After considering the respective shortcomings of copper and aluminum, some high-end radiators currently on the market often use a copper-aluminum combination manufacturing process. These heat sinks usually use copper metal bases, while the heat dissipation fins use aluminum alloy.
Of course, in addition to the copper bottom, there are also methods such as using copper pillars for heat sinks, which are based on the same principle. With a high thermal conductivity, the copper bottom surface can quickly absorb the heat released by the CPU; the aluminum fins can be made into the most conducive shape for heat dissipation with the help of complex process means, and provide a large heat storage space and rapid release, which A balance point has been found in all aspects.
Read more: The secret of heat dissipation in LED heat dissipation designBest seller SMT Machine :Qihe smt line products
-
Q10 SMT Automatic pick and place machine 10 Heads 100 Slots High Precision and High Efficiency SMT/LED Assembly
-
Q6 SMT pick and place machine 6heads 50slots With PCB Rail Servo Pick&Place Machine
-
Q4 SMT pick and place machine 4heads 50slots With PCB Rail Servo Pick&Place Machine
-
TVM802B Plus SMT pick and place machine 2heads 58slots desktop pick&place deluxe edition
-
QM10 SMT pick and place machine 10heads 80slots Fully Automatic Chip mounter SMT Assembly
-
TVM802BX SMT pick and place machine 2heads 46slots desktop pnp mounter deluxe edition
-
QL41 SMT pick and place machine 4heads 8slots LED for 1.2meters led strip pick&place machine
-
Q8 SMT pick and place machine 8heads 80slots Fully Automatic Chip mounter SMT Assembly
-
TVM802AX SMT pick and place machine 2heads 29slots desktop deluxe edition SMT Pick&Place Machine
What is SMT in engineering?
Surface mount technology is a part of the electronic assembly that deals with the mounting of electronic components to the surface of a PCB. Electronic components mounted this way are called surface-mounted devices (SMD). SMT was developed to minimize manufacturing costs while making efficient use of board space.Qihe SMT company develops and produces all kinds of SMT equipment suitable for world wide market, including pnp machine,reflow oven,stencil printer,pcb handling machines,and other smt pick and place products.
Small desktop pick and place machine TVM802A,TVM802B,TVM802AX,TVM802BX series suitable for beginners, for hobbiest or low vol usag.
Advanced level 4-head LED strip placement QL41 led machines and with rail universal series Q4,TVM925S,TVM926S,smt pick and place,pick and place
Fully automatic 6-10-head placement QM61,QM62,QM81,QM10,machines, which are suitable for high volume mass production in factories.
Know more about us https://www.qhsmt.com/about-qihe-smt-equipment/
Follow us on social media https://www.facebook.com/Qihesmt/
What is SMT in programming?
Offline Automated Programming vs Inline SMT Programming
Qihe pick and place machine can be programmed directly on the smt pick and place SMT equipment .
Or Coordinates can also be imported csv file through programming software.
Currently supported software such as protel,DXP,Altium Designer,Pads,Candes,proteus,DXP.
Inline SMT programming is a solution to consider for narrow segments of device programming requiring short programming times, with medium to high volume, for just one device smt pick and place type.
WHAT IS SMT pick and place machine?
SMT (Surface Mounted Technology) is a comprehensive system engineering technology, which covers substrates, design, equipment, components, assembly processes, production accessories and management. When it comes to SMT pick and place machines, the automatic SMT production line requires automatic loading and unloading machine, automatic solder paste printing machine, placement machine, reflow soldering machine, AOI inspection equipment, conveyor,connecting table, etc. For these SMT assembly line equipment, Qihe SMT can offer you machines in prototype SMT line, small SMT production line, mass production SMT line at low SMT line cost. Contact us now if you are interested.pick and place
WHAT IS SMT ASSEMBLY LINE?
With the development of technology, future electronic products will be lighter, smaller and thinner. Traditional assembly technology can no longer meet the requirements of high-precision and high-density assembly. A new type of PCB assembly technology-SMT (Surface Mount Technology) has emerged. SMT Assembly is the use of automated machines to assemble electronic components on the surface of the circuit board. Its density, high speed, standardization and other characteristics occupies an absolute advantage in the field of circuit assembly technology. In addition, SMT assembly has a wide range of uses.
https://www.qhsmt.com/fully-automatic-smt-pick-and-place-machine-line/